剑桥雅思10写作:Test1雅思写作task1真题+范文
发布时间:2021-02-03 关键词:剑桥雅思真题10Test 1-雅思写作Task1范文及解析
Writing Task 1
The first chart below shows how energy is used in an average Australian household. The second chart shows the greenhouse gas emissions which result from this energy use. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
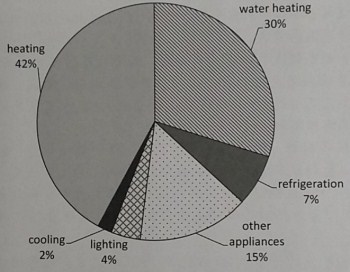
Australian household energy use
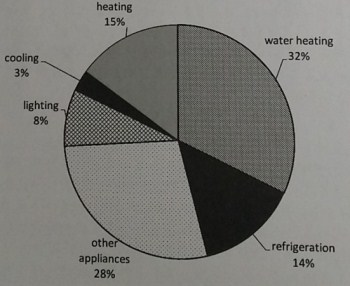
Australian household greenhouse gas emissions
a)题目分析,包括回答中需要讨论的主要特征、需要进行的对比以及考生可能对题目产生的错误理解。
要点
1.能量消耗及温室气体排放。
2.能量消耗的结构、层次以及温室气体排放的结构、层次。
考生可能产生的理解措误和问题
1.考生可能会采用过去时态而不是现在时态去描述事物发展。
2.考生也许会试图阐释家用电器的使用或提出相关建议,这两方面都是多余的。
雅思写作Task1范文
The two charts summarise the amount of energy used through various means in the average Australian household versus the amount of greenhouse gas emissions resulting from the same sources.
In the first chart, we see that the overwhelming percentage of energy is devoted to household heating, with 42% of total energy usage. The second biggest is water heating with 30%, but then the amounts drop precipitously, with other appliances, refrigeration, lighting and cooling all using 28%.
From the second chart, we learn that heating, despite being the greatest drain on energy, actually contributes relatively little to greenhouse gas emissions with 15% of the total. The greatest emitter is water heating with 32% and the smallest being cooling at 3%. The largest disparity belongs to both refrigeration and lighting, both generating twice the amount of gases from the energy they consume (7% of energy use to 14% of emissions and 4% energy use to 8% of emissions respectively).
(157 words)
两个图表总结了澳大利亚一般家庭中各种电器的耗能量以及各种电器所排放的温室气体量。
在个图表中,我们看到家用采暖的耗能占比,达到了总耗能的42%。第二位是热水器,耗能占比达30%。但其他家电、冰箱、照明及制冷等的耗能量则急剧下降,总占比只有28%。
在第二个图表中,我们发现,尽管采暖的耗能量,但实际上它所排放的温室气体相对较少,仅为总排放量的15%。的排放来源是热水器,占比达32%,而最小的是制冷,占比只有3%。的反差来自于冰箱和照明,二者所排放的温室气体量均为耗能量的两倍(分别是冰箱7%的耗能对14%的排放;照明4%的耗能对8%的排放)。




